|
In a serial system, stations are arranged so that the
first station receives the raw material for the product.
After completing processing at station 1, the partially
completed part is passed to station 2, and so on until
the finished part leaves at the last station. The three-station
example is shown in Fig. 9.
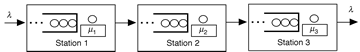
Figure 9. Three station serial system
The important thing to remember about
this system is that the output of one station becomes
the input to the next. Thus in a system with no losses,
the average arrival rate to the first station is must
equal the average departure rate from the last station.
An Extend model for a three-station system is shown
in Fig. 10. The block immediately to the right of the
generator block is a Sensor block. It gathers data and
computes the difference between the time when a part
leaves the system and the time when it enters. This
time is the cycle time and it is an important measure
of the effectiveness of a manufacturing system.
|

