Here we list the parameters associated
with single stage, deterministic inventory systems with no shortages.
All parameters are to be nonnegative. All time related parameters
must use the same time dimension.
| Inventory
The name appearing in B1 is the name for the example.
|
Data Name
The name appearing in B2 is used to name arrays on
the worksheet. It is assigned through the add-in dialog. |
Type
The type is determined by the options on the dialog. In this
case it indicates that inventory has an infinite replenishment
rate. |
| Demand rate
(D): This is the constant rate at which the product
is withdrawn from inventory. (units / time) |
| Production rate
(P): This is the constant rate at which the product
is added to inventory inventory during the production period.
(units / time). The parameter is only used for finite production
rate inventories. |
| Setup cost (A):
A common assumption is that the cost of placing an order cost
consists of a fixed cost, that is independent of the amount
ordered, and a variable cost that depends on the amount ordered.
The fixed cost is called the setup cost and given in ($). |
| Product revenue
(R): This is the unit revenue obtained when the product
is sold. This used for the profit model, but not for the inventory
cost model. ($/unit). |
| Product cost (C):
This is the unit cost of purchasing the product as part of
an order. The value is used in the profit calculation. The
value of C is used to measure the investment in the
item as it relates to holding cost. ($/unit) |
Min Quantity (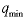 ):
This places a lower bound on the order quantity (unit) ):
This places a lower bound on the order quantity (unit) |
Max Quantity (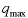 ):
This places an upper bound on the order quantity (unit) ):
This places an upper bound on the order quantity (unit) |
| Holding cost rate
(i): This is discount rate or interest rate used
to compute the inventory holding cost. The holding cost usually
includes the lost investment income caused by having the asset
tied up in inventory. This is not a real cash flow, but it
is an important component of the cost of inventory. If C
is the unit cost of the product, this component of the cost
is Ci, where i is the holding rate. (%/unit-time) |
| Other holding cost:
The holding cost may also include the cost of storage, insurance,
and other factors that are proportional to the amount stored
in inventory and the time an item remains in inventory. In
the following we use H as the holding cost per unit
including both the lost investment income (Ci) and
other holding cost. ($/unit-time) |
| Lead time (L):
This is time interval between when an order is placed and
when the inventory is replenished. (time) |