|
|
 |
Process
Flow Optimization |
 |
-
Resources and Materials |
|
|
|
The second option produces
a linear programming model that adds to the product variables,
variables that specify the time used on each resource
and the amounts of each raw material. It includes constraints
on the amounts of raw materials and the amounts of resources
available. It determines the optimum product mix with
these constraints included. |
Clicking OK presents
the Linear Model dialog shown below. As for the LP1 model,
the number of variables and number of constraints can be increased,
but not decreased.
|
| |
|
| |
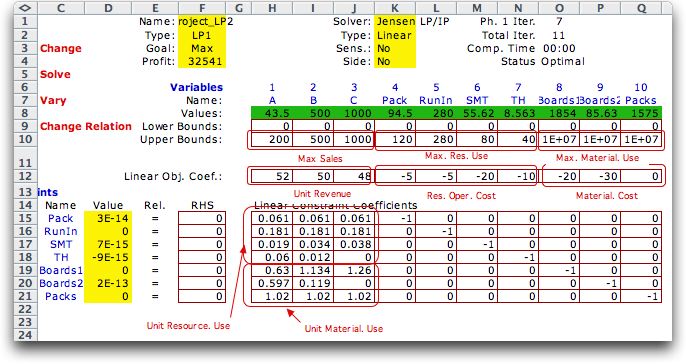
The figure below shows
the model constructed with the second model option. The data
for the model is derived directly from the data on the Project
Worksheet. The model produced can be solved with the built in
Excel optimizer (Solver add-in) or the LP Solver Add-in. The
solution shown is the optimum product mix for the example. In
addition to the sales value, the hours required for the resources
and the amounts of the raw materials are explicitly displayed
in the variable value row of the LP solution. The model allows
simple upper bounds for the raw material amounts and resource
times. |
| |
 |
| |
The optimum sales quantities are transferred
to the Sales column on the Project worksheet. The numbers
in the column are linked by formula to the Project LP2 worksheet,
and the column is colored yellow. When features of the LP model
are changed and the model solved, the solution is reflected
in the sales column. The user can change numbers in the sales
column, but the automatic links to the Project LP2 worksheet
are lost. |
| |
|
| |
|
|