| |
Facilities for populating printed
circuit boards are generally configured as flow lines. A simplified
version of a facility for board manufacture is shown in the
figure. The first station is where raw boards are inspected
and marked, and component kits are prepared. Let us assume that
the orders arrive at the rate of 60 boards per hour and that,
on average, 80 boards can be processed per hour. A certain fraction,
5%, must be recycled through this stage to correct defects,
while 75% move on to the surface mount technology (SMT) center
and the remaining 20% go to the through-hole center. Station
2 consists of 3 SMT robotic placement machines that can each
process an average of 30 boards per hour. It receives input
from both the preparation area and from outside customers. Station
3 has a single through-hole (T-H) machine that operates at an
average rate of 20 boards per hour.
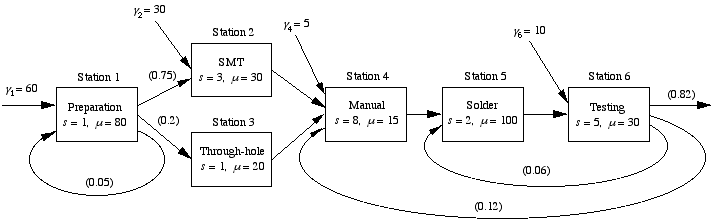
After the small components are placed on the boards, they all
go to a manual workstation staffed by 8 operators who perform
a preliminary inspection and attach large components, such as
heat sinks and batteries. Each operator can process 15 boards
per hour on average. Next, at station 5, the boards flow through
a wave solder machine that has a capacity of 100 boards per
hour. There are two solder machines operated in parallel. Boards
are also cleaned and touched up at this stage. At station 6,
testing on one of five parallel machines is conducted to look
for opens and shorts, and to determine if the boards function
correctly. The testing rate is 30 per hour. On average, 6% of
the boards must return to station 5 for additional soldering
and 12% to station 4 for rework. The remaining 82% pass all
tests and are shipped.
Construct the process flow model for this situation. Find the
utilization of each of the machines, total throughput time and
WIP for the system.
Assume all interarrival times and service processes have exponential
distributions with mean values determined by the rates given
above. Add queues for each station. Find the utilization of
each of the machines, total throughput time and WIP for the
system.
|

