The Inventory
add-in also has a function to estimate average Work in Progress
(WIP) for components of a system. The general call to this
function is written as below with two arguments.
Inv_WIP(instance As Range, inventory
As Range)
Both arguments are ranges. The instance is a range
that specifies the variables controlling the component. The
range inventory holds the parameters associated with
the component that are necessary to compute the WIP and related
results.
Several different types of components are
analyzed by the same function. The worksheet below shows the
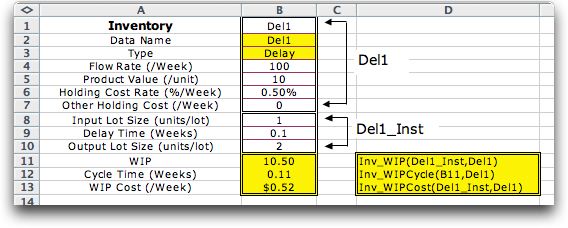
results a delay, one of the simplest of the components. The inventory range
is B1:B7 and has the name Del1. The type of the component is
in B3, Delay. The WIP functions interpret the remainder
of the range based on this type. The instance range
is B8:B10 and has the name Del1_Inst. The controlling variables
are the input lot size (1), the delay time (0.1 week) and the
output lot size (2).
The WIP for this component is computed by the function is
cell B11.
= Inv_WIP(Del1_Inst,Del1)
An alternative entry would enter the ranges explicitly.
= Inv_WIP(B8:B10,B1:B7)
Although the data is arranged by column here,
the function also accepts a row orientation. The value, 10.50,
is the average level of WIP inventory caused by this delay.
Two other WIP related quantities are computed in the example
with two additional functions. The first computes the average
residence time, which is typically called cycle time in WIP
analysis. The second computes the holding cost associated with
the WIP. General call statements are below.
Inv_WIPCycle(Inv_L, inventory As Range)
Inv_WIPCost(instance As Range, inventory
As Range)
The first argument of the Inv_WIPCycle function
is a pointer to the cell holding the average WIP.
The figure below illustrates another component
type, Process, which represents a processing operation
in a manufacturing system. Although the call statements the
WIP functions are the same, the inventory range is
larger for this component to accommodate parameters relevant
to a processing operation. The instance range still
has three cells, but the middle cell, B29, now shows the processing
lot size.
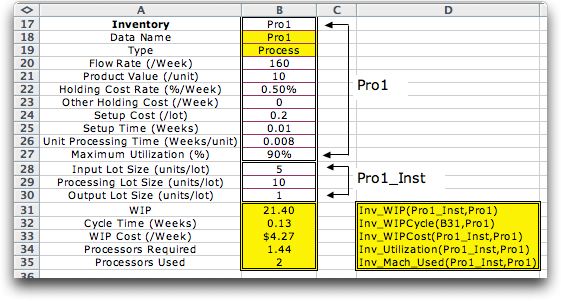
The results of the WIP function appear in cells
B31 through B35. Two new functions are introduced here to compute
the processor utilization and the integer number of processors
required to accommodate the flow. The general call statements
show that have the two range arguments.
Inv_Utilization(instance As Range,
inventory As Range)
Inv_Mach_Used(instance As Range, inventory
As Range)
Although Excel formulas or functions can implement
special cases of the results, we use functions to provide generality.
Because the functions use all the data and variables associated
the system, they can be used without the data forms constructed
by the add-in.
The WIP functions recognize seven different types
of components as illustrated in the figure below. We show with
x's data that is irrelevant for certain of the components.
The middle cell of the instance variables has different
meanings for the different components. The Change component
does not use the middle cell. |