| |
Maximization of a
convex objective function with linear constraints leads to difficulties
because the continuous problem has local maxima that may not
be global minima. We consider again the nonlinear program given
earlier, but allow the variables to be continuous. The figure
below shows the solution obtained with the Excel Solver starting
from all 0's in the Values row. The Solver terminates
immediately because this solution is a local maximum. |
| |
| |
Unfortuantely, this solution is
not the global optimum. A common method to overcome this is
to search for the global optimum by repeatedly using a nonlinear
solver with different starting points. The Optimize
add-in automates this process. Select Math Program
from the Optimize menu and choose NLP Start from the
options.
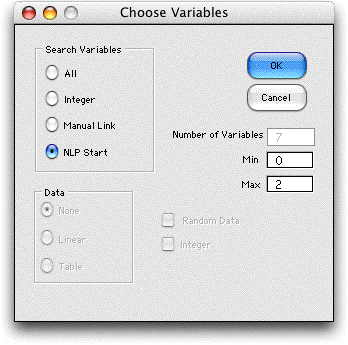
A combinatorial form is constructed with a variable
for each of the original NLP variables. This form is used to
generate alternative starting solutions for the NLP. The add-in
generates random discrete values between the lower and upper
limits, places the results into the Value array of
the NLP model and uses the Excel Solver to search for the local
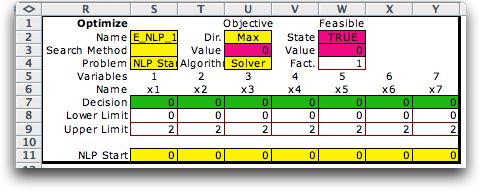
optimum. The Factor in cell W4 multiplies the discrete values
in row 7 to obtain the starting solution in row 11. In the present
case a factor of 1 is satisfactory. For other cases it may be
necessary to choose a factor that makes the starting solutions
representative of the range of solutions in the feasible region.
|
| |
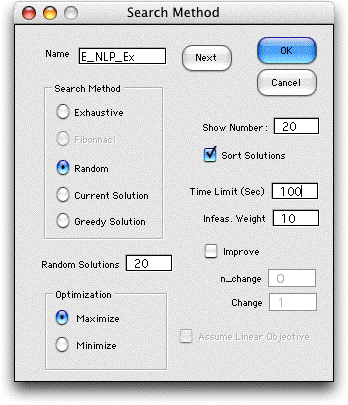
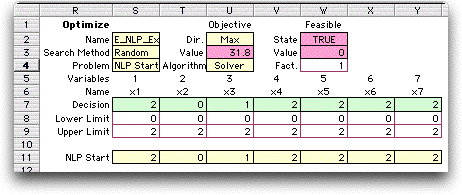
To search for the global optimum,
we choose Random as a search method and choose 20 as the number
of solutions to generate.
The figure below shows the combinatorial form
for the last iteration. These values provide the starting solution
for the Excel Solver.
|
| |
The solution obtained with the
starting solution is the one below. This is the global optimum. |
| |
| |
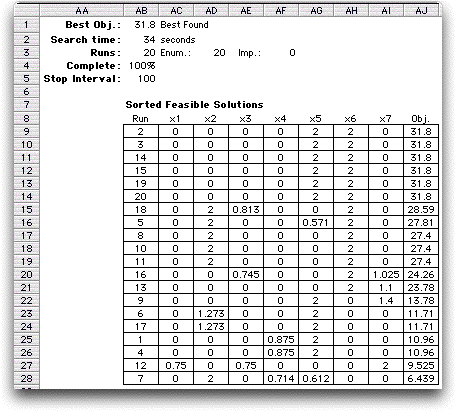
The sorted solutions obtained from the 20 runs
are shown below. Although the optimum was found by several starting
solutions, several other local optimum were also discovered.
For the NLP Start option, the solutions stored in this table
are the local optimum solutions found rather than the discrete
starting solutions. The Excel Solver seems to have a random
element that can find different local optima from the same starting
solution. |
| |
 |
| |
There is no guarantee that the global optimum
will be found with this procedure, but certainly the result
is much more likely to be optimum that a single run taken from
an arbitary start.
The add-in was not successful in calling the Excel Solver
with this add-in using Office X on a Mac. The method seems
to work with Excel 2001 on a Mac or Excel XP using Windows.
Other combinations have not been tested. |
| |
|